
A global knowledge ecosystem of students, professionals & industry-leaders to share, create, and mentor experiences
contact@podareduspace.org
+91 98202 27795

Technological Innovation and Customer Engagement strategies by NIO in the Chinese Market by Keyaan Vastani
To what extent has NIO’s technological innovation and customer engagement strategies contributed to its success in the Chinese EV market?”
Research Question:
“To what extent has NIO’s technological innovation and customer engagement strategies contributed to its success in the Chinese EV market?”
1. Introduction
The rise of electric vehicles marks a pivotal shift in the automotive industry, merging sustainability with dynamic technology. As the world continues to deal with climate change, EVs represent a practical solution by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting renewable energy adoption in China, the largest EV market globally ((Statista); (McKinsey)), this transformation is particularly pronounced, with the government and private sector prioritizing innovation and accessibility to achieve environmental goals (McKerracher). NIO Inc., founded in 2014 by William Li, is a leading company in this market. NIO, based in Shanghai, has made a name for itself in the development of battery-swapping technology (Lin et al.) allowing users to replace spent batteries with fully charged ones in a matter of minutes. This technological innovation has addressed the long-standing range anxiety issue, a significant deterrent to EV adoption, and reflects the company's commitment to innovation. For that reason, NIO excels through customer engagement such as initiatives like NIO House and NIO day that make a community, increase loyalty to the brand from their consumers.
This essay analyses the extent to which NIO's technological innovation and strategies for customer engagement have brought success to the company as a leader in the intense Chinese EV market. Exploration of NIO's market performance along with the analysis of its strategic initiatives and comparison with industry trends will give insights into the critical role these elements play in shaping NIO's position as a leader in the market. Additionally, the paper will touch on broader((Lin et al.) implications for the global EV industry and the sustainability agenda
Nio PLC Vehicle Deliveries for the years 2021-2023:

NIO has experienced an enormous growth curve from 2021 to 2023 of the way of thinking and executing well in the process for them to succeed among one of the fastest-evolving electric-vehicle markets to date. The company was able to deliver 91,429 vehicles-on more than double its deliveries of last year, it was showing a sensational 109 percent year-over-year growth at the end (“Nio Annual Report 2022”). There are a few notable reasons that led to an increased delivery of the two vehicles first; there was an increase in range of products by NIO comprising luxury electric SUVs: ES8, ES6, and EC6 (Team). Such varieties attracted more clients as luxury electric SUVs were in hot demand. This was almost as if they were seeking to be seen with something so diverse and would be a best comparison available within the same avenues.
Another factor that proved to be in its favor for NIO was its innovative launch of the "Battery as a Service" model that changed how the customers see electric vehicles (Porter).BaaS has allowed customer users to replace the battery of the vehicle instead of charging it, hence basically offering more convenience and flexibility in its use. This technology also brought the entry price of NIO vehicles to an enormous extent, making them owning affordable for a greater proportion of customers. The BaaS model attracted low-price-conscious buyers and established NIO as an innovator in EVs because it solved the industry's pressing issue of battery management. To offer BaaS, NIO tackled all the issues of cost and time related to charging. It further opened the gateway of attractive EVs and electric vehicles into the channel by stretching it to a larger number of buyers.
NIO delivered 122,486 vehicles in 2022 with continuous growth momentum (“NIO Inc. Reports Unaudited First Quarter 2023 Financial Results”). Year-on-year, the growth rate of NIO remained at 34%. It is an astonishing achievement considering the huge success the SUV series experienced again. In fact, this pushed ahead with new additions- ET7, a smart electric sedan that brought yet another type to the mix again. The new customers that have really come pouring into the doors with the ET7 have really helped NIO build a stronger ground in the luxury electric sedan area. Infrastructural investments through betterment of its network of battery-swapping stations and charging solutions are quite substantial (Porter). This investment has helped make ownership of EV practical with services to further the rising tide of customer convenience and satisfaction. Besides all these investments into infrastructures, NIO expanded sales and service network, thus using the best possible platform for sustainable long-term growth. Thus, at that point in time when all of the world's supply chains continued to be in limbo, the company managed to continue growing.
By the end of year-end 2023, NIO had not yet reached its targets of delivering 160,038 units; this marked their third consecutive year posting double-digit growth growth rates but this time with a growth rate of 30.7% (“Nio Annual Report 2022”)& (NIO, “NIO Inc. Reports Unaudited Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2023 Financial Results”). This has led to an affirmation that NIO has the capability to scale even in an environment characterized by market volatility, supply chain challenges, and a rising level of competition. The real competitive benefit of NIO lies in technological brilliance, mainly in the evolution of autonomous driving capabilities and, not to forget, the company's battery-swapping technology. All these helps place NIO at the apex of its peers in a competition within the EV sector, and also express the meaning of NIO having a central position in technological advancements in the automotive market.
In total, NIO, by the end of 2023, was able to deliver nearly 450,000 vehicles (IEA), so that the company has experienced phenomenal growth and had highly expanded the scope of the market. NIO was therefore resolute and pliable enough to demonstrate very strong strategic leadership in a very complex environment marked by short-term chip shortages and unstable market conditions. From an infrastructural point of view, innovative technologies, expansions in the product lines, and growth have helped to boost the position of this firm as the front-runner in the global EV market. Today, in the corporations, a combination of effective execution and visionary strategies has led to significant success for NIO in the electric vehicle market, with high competition.
2. Methodology
This essay is primarily based on secondary sources in the analysis of strategies applied by NIO Inc. to maintain growth in the competitive Chinese EV market.
Key sources are:
1. Annual reports and corporate communications of NIO: These reports present the all-round data regarding financial health of NIO, operational milestones achieved, and strategic initiatives pursued by the company. Specifically, they highlight the technological innovations of the company, such as its battery-swapping technology and sustainability goals. Annual reports contain a comprehensive statement of financial position and an MD&A section that provides the reader with an understanding of strategic direction and the company's position in its industry. Being public documents that are regulated by authorities, they provide a high level of transparency, making them a reliable source of primary data (“Nio Annual Report 2022”).
2. Market Analysis Reports: These reports are done by industry analysts such as McKinsey & Company and BloombergNEF. They put NIO's performance into context by providing a backdrop of the overall trends in the EV market. They aid in competitor benchmarking, consumer demand forecasts, and government incentives for electric vehicles. They play an important role in the assessment of external factors affecting NIO's operations, like the increasing adoption of electric vehicles in China and emerging technological advancements, such as autonomous driving (McKinsey).
3. Financial Databases Bloomberg and GlobalData contain up-to-date and historical data on NIO's financial performance metrics, including liquidity ratios, earnings per share, and stock price trends. This allows for a quantitative assessment of the firm's financial health and operational performance. Compared to peer firms like Tesla and
BYD, these databases offer an even deeper insight into its standing in the market (“NIO Inc. (NIO) Stock Price, News, Quote & History - Yahoo Finance”).

4. Public Filings and Press Releases: NIO's quarterly reports, SEC filings, and corporate press releases provide current information concerning the operational progress of NIO, new partnerships, and product launches. These are sources that provide supplementary information to follow NIO's short-term performance and strategic moves in enhancing the general analysis (Washington). By combining these sources, this essay creates a comprehensive view of NIO’s strategies, allowing for an in-depth analysis of its technological innovation and customer engagement initiatives.
3. Data Figures
Rationale for Analytical Tools
1. SWOT Analysis This tool is helpful for analyzing the internal strength and weakness of NIO such as battery-swapping technology and domestic market dependency, while considering external opportunities and threats. The primary usage of SWOT is identifying action items that are ready to be improved upon and alignment with market opportunities (Gurel).
2. PESTLE Analysis: The PESTLE model highlights the most relevant external determinants of NIO's operations. Politically, NIO's growth was further supported through government aid and investment in infrastructure for EVs, although changes in policy will tend to affect demand going forward. The economic factor is that with disposable incomes increasing in China, NIO's premium EVs have become affordable; however, economic slowdowns may challenge NIO to rely on high-income consumers. Socially, NIO's sustainability initiatives of recycling the batteries and working toward net-zero carbon are matched with growing environmental awareness so will attract environment-conscious buyers. Technological advancement in such areas as autonomous driving and solid-state batteries provides some opportunities but comes with large R&D costs. The law also comes in here because it necessitates emissions and safety compliance for a market opening. This raises costs on the operating side. Environmentally, there is pressure to reduce carbon footprints, which enhances NIO's market position as it adopts eco-friendly manufacturing practices and renewable energy sources (McKinsey); (IEA).
3. Financial Ratio Analysis: NIO's current financial performance reflects its strengths and challenges. The current ratio of 1.6 in 2023 indicated strong liquidity, which gave NIO the ability to meet short-term liabilities, however, this requires efficient management of working capital. Revenues have grown, though profit margins have been limited because of high production costs that require operational efficiencies.
Levels of debt have increased mainly to fund R&D and infrastructure but pose risks when not managed effectively. NIO's performance with volatile market shows how importance constant results make towards getting longer-term investors. Solving these financial and external challenges will give NIO robust resilience that enables them to take advantages from all of the upcoming opportunities that present themselves in this very competitive EV market (“Electric Vehicles Market Analysis by Region, Propulsion Type (BEV, FHEV, MHEV, PHEV, EREV, FCEV), End-User Type (Personal, Commercial) and Forecast, 2021-2030”).
4.Porter's Five Forces Analysis: This tool analyzes competitive pressure in the EV space such as the threat of new entrants, power of suppliers, and industrial rivalry that gives an insight into how NIO stands in a market position compared to their peers Tesla and BYD(Porter).
Using these tools, this essay critically evaluates NIO's strategies to determine their effectiveness in driving growth and sustaining market leadership.
Market Share
NIO currently commands an approximate 14% of the electric vehicle market in Chinaa strong market share that makes it a serious challenger for considerable players such as BYD and Tesla. This percentage proves strong presence in one of the biggest electric vehicle markets in the world, which speaks of NIO's capability to innovate and differentiate. The company has emphasized innovative features such as battery swapping technology and advanced driver-assistance systems to differentiate its products (“Thailand: Commercial Energy Production by Source 2023 | Statista”). Hence, NIO stands out from competition for this particular brand, symbolizing luxury, performance, and cutting-edge technology for the high-end consumer looking for prime quality EVs(InsideEVs, 2024). In addition, alliances with battery manufacturers and tech companies have helped further solidify NIO's product lines and supply chain with respect to efficiency (McKinsey).
Current Ratio
NIO's current ratio, recorded at 1.6 for 2023, indicates strong capacity to cover shortterm liabilities with current assets. A current ratio above 1 is generally viewed as a good indicator of a positive financial health, thus revealing that NIO is less vulnerable to any short-term financial crises in the highly volatile automotive market (“Electric Vehicles Market Analysis by Region, Propulsion Type (“Electric Vehicles Market
Analysis by Region, Propulsion Type (BEV, FHEV, MHEV, PHEV, EREV, FCEV), EndUser Type (Personal, Commercial) and Forecast, 2021-2030”). Therefore, this solid liquidity position hence improves investor confidence, allowing for more operational flexibility in investments into growth opportunities as well as financial resilience when it comes to managing cash flow needs (“NIO Inc. (NIO) Stock Price, News, Quote & History - Yahoo Finance”).
Position Map
A position map will creatively present NIO's competitive landscape with respect to price and quality. The company tends to brand itself as an expensive brand, where the cost of vehicles is always slightly higher than most other mass-market EVs, based on its utilization of premium materials, cutting-edge technology, and excellent customer service. Quality-wise, most of the performance, technology, and user experiences of NIO vehicles come close to those from luxury automotive brands (Lin et al.). Taking into consideration the more affordable, widely available models by BYD, while Tesla brings flagship status and performance with innovative technology, NIO fights a segmental space for luxury EVs that fulfill demand from customers who are willing to pay a higher price for quality and exclusivity (McKinsey).
SWOT Analysis
Strengths Weaknesses
Innovative battery-swapping tech High production costs
Strong brand identity and loyalty Limited presence in global markets
Strategic partnerships with tech firms Heavy reliance on domestic market
Opportunities Threats
Increasing demand for EVs Fierce competition in the market
Government incentives for EV adoption Regulatory hurdles
Expansion potential in international
Rapid changes in technology
markets
PESTLE Analysis
● Political: Government initiatives to support electric vehicle adoption through subsidies and incentives.
● Economic: Rising disposable incomes among consumers in China are
facilitating EV purchases.
● Social: Growing environmental awareness is leading consumers to prefer sustainable transportation options.
● Technological: Rapid advancements in battery technology and autonomous driving are reshaping the industry.
● Legal: Compliance with stringent emissions regulations is crucial for maintaining market position.
● Environmental: Increasing pressure to reduce carbon emissions and promote
sustainability.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis
1. Threat of New Entrants: Moderate, as the high initial investment in technology and manufacturing can deter new competitors.
2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers: High, due to a limited number of suppliers for critical components like batteries.
3. Bargaining Power of Buyers: High, as consumers have a variety of options to choose from.
4. Threat of Substitute Products: Moderate, with traditional vehicles and public transport providing alternatives.
5. Industry Rivalry: Very high, with many established and emerging players vying for market share.

Tesla and BYD lead the global electric vehicle market with 19.9% and 17.1% market shares, respectively, driven by scale, innovation, and international reach. In contrast, NIO holds a smaller 1.7% share, focused on China's premium EV segment, competing with brands like BMW and Mercedes-Benz in luxury markets. With strong competitors such as Volkswagen and Hyundai targeting mass-market EVs, NIO faces pressure but differentiates itself through innovations like battery-swapping technology and a usercentric approach, positioning it for gradual growth in an increasingly competitive landscape
4. Strategic Initiatives
Technological Innovation
At NIO, technological innovations are at the forefront, especially in using its batteryswapping technology by which customers can replace its batteries in minutes. Battery swapping helps to alleviate range anxiety-a common concern among ev buyers-and enhances customer satisfaction. The company's use of a "Battery as a Service" (BaaS) model lowers the upfront cost of owning one of its vehicles, promoting access to EV ownership through the management of battery-related longevity and cost (Lin et al.). NIO's investment in autonomous driving and the next generation of battery technology puts it in a favorable position to compete in a rapidly changing EV market.
Customer Engagement
Customer engagement is at the heart of NIO's strategy. A NIO Day event introduces new products, while the NIO House provides opportunities for networking and learning to foster brand loyalty. The NIO Day creates an emotional connection with customers while NIO House provides opportunities for workshops and connections. It goes further by allowing car control, event updates, and an interface to the community in its app.
This puts NIO as a brand beyond being a car company, ensuring customers' loyalty
(Lin et al.)
Sustainability Efforts
NIO aims to reach net-zero carbon footprint by 2030. The company focuses on using recyclable materials and environmentally friendly practices in its manufacturing processes, while battery recycling programs reduce the impact on the environment. It also invests in renewable energy to power battery-swapping stations and production facilities, aligning its operations with global sustainability goals. Its collaborations with policymakers further establish NIO as a leader in clean energy adoption, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and driving the EV industry toward sustainability (NIO, “NIO Inc. Reports Unaudited Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2023 Financial Results”).

Strategic Partnerships
NIO collaborates with technology firms like Baidu for autonomous driving and Intel for software development. It also utilizes external expertise to hasten innovation, such as through partnerships with CATL in the development of efficient and durable batteries. Operations are streamlined and resilience to supply chain challenges is guaranteed through these partnerships. Time-to-market for new technologies is reduced and consumer demand is met through such strategies that make NIO stronger on its technological edge and lay down the foundation for future growth in domestic and international markets (Lambert); ---. (NIO, “NIO Inc. Reports Unaudited Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2023 Financial Results”)
5. Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
Case Study: International Expansion
NIO's successful entry into the European market is a testament to its effective growth strategies. The launch of the ES8 model in Norway marked NIO’s first step outside China, showcasing its capability to adapt to different markets. The Norwegian government’s supportive policies for EV adoption further aided this expansion. This case illustrates how NIO can leverage governmental support to enhance market penetration.
Example: Customer Satisfaction
A recent survey revealed that over 90% of NIO users expressed satisfaction with the battery-swapping service. Many customers highlighted the convenience and efficiency of the service, which significantly enhances the overall ownership experience. This positive feedback illustrates how NIO’s strategic focus on customer needs translates into brand loyalty.
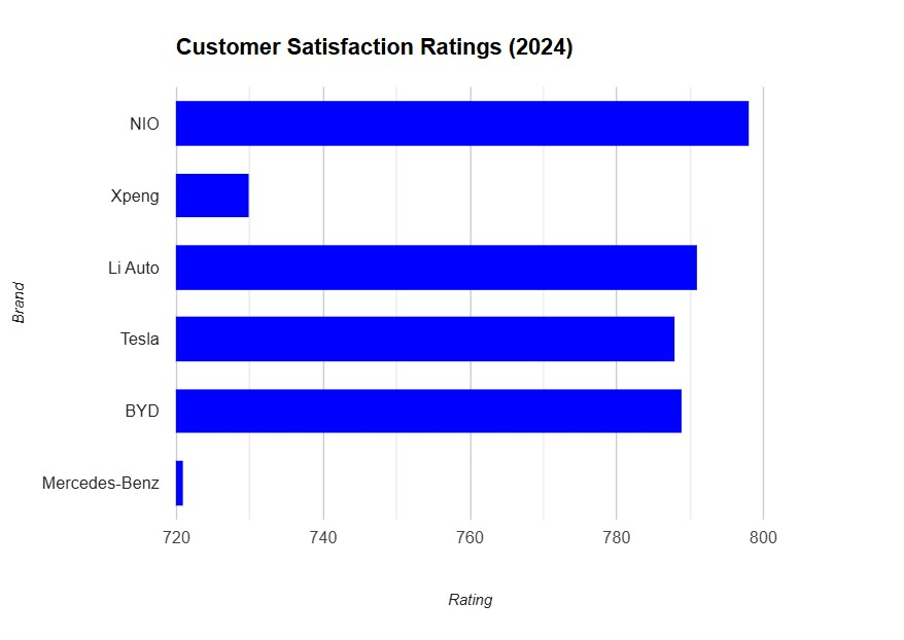
From the 2024 customer satisfaction ratings, it is evident that electric vehicle brands dominate the industry. NIO leads in ratings with 798 and 788 respectively in the J.D. Power 2024 EV Customer Satisfaction Study. These ratings reveal that NIO has maintained a quality level and ensured satisfaction of its customers over the years, probably because of the integration of latest technologies with reasonable costs and after-sales service.
Next in line are XPENG, Li Auto, and BYD, which have scored 791 and 789, respectively (Kothari).The close grouping indicates the strong competition within the EV segment, with innovation and customer satisfaction as the key distinguishing factors. These brands are gaining fast and threatening the market share of the big players, such as Tesla and the traditional auto makers.
Tesla is a market leader in the EV segment and has received a score of 787, which is below that of its competitors (McKerracher).
This means that while Tesla remains one of the leading companies, it might be losing its competitive edge. The increasing number of viable alternatives may be compelling Tesla to innovate even more to improve areas such as pricing, product variety, and customer service.
Whereas the luxury brand Mercedes-Benz lags at 771, underperformance could
indicate the difficulties faced by the traditional automaker in transitioning to the rapidly growing electric and sustainable vehicles. Consumer preferences are turning to EVs, so a traditional legacy brand like Mercedes-Benz has to speed up the transition toward cleaner technologies and redefine their value propositions for competitive edge.
In short, 2024 ratings depict a world in which the automotive landscape has shifted. The innovation coupled with customer-centric features places EV brands at the forefront of this shifting industry. Traditional automakers must move quickly to catch up with this shifting landscape.
The 2024 customer satisfaction ratings provide valuable insights into the shifting dynamics of the global automotive industry, particularly highlighting the rise of electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers. Among the contenders, NIO has firmly established itself as a frontrunner, with top scores of 798 and 788. This strong performance reflects NIO's strategic positioning within China's highly competitive EV market. By prioritizing technological innovation, sustainability, and customer-centric solutions, NIO has not only captured market share but has also solidified its reputation as a leader in the EV industry.
One of NIO's key strengths lies in its commitment to cutting-edge technology and its focus on creating a seamless ownership experience. The company’s integration of advanced features such as battery swapping technology, over-the-air software updates, and AI-driven driving assistance systems has set it apart from its competitors.
Additionally, NIO’s robust customer engagement initiatives, such as exclusive memberships and its thriving online community, have fostered a loyal customer base. This dual emphasis on innovation and engagement ensures that NIO not only meets current consumer expectations but also anticipates future trends, keeping it ahead of the curve.
Close on NIO’s heels are other prominent EV brands such as XPENG, Li Auto, and BYD, with scores of 791, 791, and 789, respectively. These brands demonstrate the growing competition in the EV sector, where every manufacturer is striving to offer cutting-edge features and high-value propositions. XPENG’s focus on autonomous driving technology and affordability, along with Li Auto’s hybrid-electric offerings catering to families, have enabled them to secure strong positions in the market. Similarly, BYD's extensive experience in battery manufacturing and its diverse EV lineup have made it a formidable competitor. The neck-and-neck competition among these brands underscores the rapid evolution of the EV market in response to consumer demand for sustainable and technologically advanced vehicles.
Tesla, a pioneer in the EV market, scored 787, slightly below the top competitors. While Tesla remains a global leader in innovation and brand recognition, these ratings suggest that its dominance is being challenged, particularly in China, the world’s largest EV market. With local competitors offering increasingly competitive pricing and features, Tesla must address areas such as localization, affordability, and customer service to maintain its stronghold. While its core strengths, such as its Supercharger network and Autopilot systems, continue to attract customers, Tesla faces the challenge of adapting to an increasingly crowded market with rapidly maturing competitors.
In contrast, Mercedes-Benz, despite its long-standing reputation as a luxury automaker, scored a relatively low 771. This underperformance highlights the challenges faced by traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) manufacturers in transitioning to the EV era. Mercedes-Benz’s lower ratings may stem from its slower pace in developing electric models compared to pure EV players. While the brand is making strides with its EQ series, the results suggest that customers are prioritizing innovation, sustainability, and value over legacy prestige. To stay competitive, traditional automakers like Mercedes-Benz will need to accelerate their electrification strategies and invest heavily in customer-centric innovation to meet evolving expectations.
NIO’s approach to sustainability is also noteworthy. Beyond offering zero-emission vehicles, the company has implemented strategies to reduce its overall carbon footprint through green manufacturing processes and renewable energy integration. Furthermore, its strategic partnerships with technology and energy companies have positioned it to expand globally, with plans to enter markets in Europe and beyond. This international focus will not only boost NIO's revenue streams but also enhance its brand visibility on a global scale.
Conclusion
2024 customer satisfaction ratings reflect the fact that consumers have increasingly opted for more electric vehicles as these represent innovation and sustainability and are cheaper. Unwavering involvement in innovation has seen leaders to their position with examples such as NIO success stories on the EV business market. Examples that currently challenge this include XPENG, Li Auto, and BYD. The giants like Tesla and classic producers must be innovative by setting more challenges for themselves by raising their stakes. The game in the automobile industry has changed; it is no longer about legacy and heritage but agility, innovation, and ability to meet the rapidly changing consumer demands.
Brands that succeed in this transformative period shall be those that adapt quickest and prioritize customer satisfaction to leap toward a more sustainable future with advanced technology. For this reason, NIO's strategic vision and successful execution place it at the fore of this revolution, hence setting a benchmark for all others.
7. Works Cited
1. “2024 Electric Utility Business Customer Satisfaction Study.” J.D. Power, 13 Nov. 2024, www.jdpower.com/business/press-releases/2024-electric-utilitybusiness-customer-satisfaction-study. Accessed 20 Nov. 2024.
2. Cheng, Evelyn. “EV Company Nio Aims to Build Battery Chargers and Swap Stations in Every Chinese County.” CNBC, 21 Aug. 2024,
www.cnbc.com/2024/08/21/ev-company-nio-to-build-battery-chargers-swapstations-across-china.html. Accessed 10 Sept. 2024.
3. “China Electric Vehicle Market Report 2023.” Researchnreports.com, 2024, www.researchnreports.com/reports/China-Electric-Vehicle-Market-2023.
Accessed June 2024.
4. “Electric Vehicles Market Analysis by Region, Propulsion Type (BEV, FHEV, MHEV, PHEV, EREV, FCEV), End-User Type (Personal, Commercial) and Forecast, 2021-2030.” Market Research Reports & Consulting | GlobalData UK
Ltd., 25 Apr. 2024, www.globaldata.com/store/report/ev-market-analysis/. Accessed 9 Aug. 2024.
5. “Form 20-F for NIO INC Filed 04/28/2023(Annual Report).” NIO, 28 Apr. 2023, p. 506, ir.nio.com/static-files/a5408c40-1840-488c-9658-dcf5e21c9665. Accessed 5 July 2024.
6. Gurel, Emet. “SWOT Analysis: A Theoretical Review.” Journal of International Social Research, vol. 10, no. 51, Aug. 2017, pp. 994–1006,
http://dx.doi.org/10.17719/jisr.2017.1832.
7. IEA. “Global EV Outlook 2023 – Analysis.” IEA, Apr. 2023,
www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2023. Accessed 12 July 2024.
8. Kothari, Suvrat. “U.S. EV Sales Hit Another Record in Q3 2024: ’10% Share within Reach’.” InsideEVs, 13 Oct. 2024, insideevs.com/news/737158/us-evsales-q3-2024/. Accessed 20 Nov. 2024.
9. Lambert, Fred. “Electric Vehicle Startup NIO Raises ‘up to $600 Million’ in
Latest Round Led by Baidu.” Electrek, 27 Mar. 2017,
electrek.co/2017/03/27/electric-vehicle-startup-nio-raises-up-to-600-millionbaidu/. Accessed 20 July 2024.
10. Lin, Shu, et al. A P R I L 2 2 , 2 0 2 2 NIO: A Chinese EV Company’s Global Strategy. 22 Apr. 2022. Accessed 30 June 2024.
11. McKerracher, Colin. “Electric Vehicle Outlook 2023 .” Bloomberg NEF, 2023,
about.bnef.com/electric-vehicle-outlook/. Accessed 10 July 2024.
12. McKinsey. “New EV Entrants Disrupt Europe’s Automotive Market | McKinsey.” Www.mckinsey.com, 2022, www.mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-andassembly/our-insights/new-ev-entrants-disrupt-europes-automotive-market.
Accessed 11 July 2024.
13. NIO. “ANNUAL REPORT NIO INC 2024.” NIO, 4 Sept. 2024, p. 503,
ir.nio.com/static-files/b9974b9f-e057-41aa-be67-97f41e5c0d82. Accessed 5 July 2024.
14. ---. “NIO Inc. Reports Unaudited Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2023 Financial Results.” NIO, 5 Mar. 2024, p. 12, ir.nio.com/system/filesencrypted/nasdaq_kms/assets/2024/03/05/5-03-
46/NIO%20Inc.%20Reports%20Unaudited%20Fourth%20Quarter%20and%2
0Full%20Year%202023%20Financial%20Results.pdf. Accessed 2 July 2024.
15. ---. “NIO Inc. Reports Unaudited Third Quarter 2023 Financial Results.” NIO, 12 May 2023, p. 10, ir.nio.com/static-files/2bc5b8b8-1dcc-4185-bb44bedfb3528797. Accessed 2 July 2024.
16. “Nio Annual Report 2022.” NIO, 2022, p. 506, ir.nio.com/static-files/a5408c401840-488c-9658-dcf5e21c9665. Accessed 6 July 2024.
17. “NIO Inc. (NIO) Stock Price, News, Quote & History - Yahoo Finance.” Finance.yahoo.com, finance.yahoo.com/quote/NIO/. Accessed 30 July 2024.
18. “NIO Inc. Reports Unaudited First Quarter 2023 Financial Results.” NIO, 9 June
2023, p. 9, ir.nio.com/system/files-
encrypted/nasdaq_kms/assets/2023/06/09/6-03-
10/NIO%20Inc.%20Reports%20Unaudited%20First%20Quarter%202023%20 Financial%20Results.pdf. Accessed 30 June 2024.
19. “NIO Inc. Reports Unaudited First Quarter 2024 Financial Results.” NIO, 6 June
2024, p. 9, ir.nio.com/system/files-
encrypted/nasdaq_kms/assets/2024/06/06/6-14-
51/NIO%20Inc.%20Reports%20Unaudited%20First%20Quarter%202024%20 Financial%20Results.pdf. Accessed 5 July 2024.
20. Porter, Michael E. “How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy.” Harvard Business Review, Mar. 1979, hbr.org/1979/03/how-competitive-forces-shapestrategy. Accessed 30 June 2024.
21. Public , NIO. “NIO Inc. Reports Unaudited Second Quarter 2023 Financial Results.” NIO, 29 Aug. 2024, p. 11, ir.nio.com/system/filesencrypted/nasdaq_kms/assets/2023/08/29/6-17-
47/NIO%20Inc.%20Reports%20Unaudited%20Second%20Quarter%202023
%20Financial%20Results%20.pdf. Accessed 1 July 2024.
22. Statista. “Electric Vehicles - Worldwide | Statista Market Forecast.” Statista,
2024, www.statista.com/outlook/mmo/electric-vehicles/worldwide. Accessed 2024.
23. Team, Trefis. “What’s Happening with Nio Stock?” Forbes, 4 Dec. 2024, www.forbes.com/sites/greatspeculations/2024/12/04/whats-happening-withnio-stock/. Accessed 6 Dec. 2024.
24. “Thailand: Commercial Energy Production by Source 2023 | Statista.” Statista, 2023, www.statista.com/statistics/1267855/china-electric-vehicle-marketshare/. Accessed July 2024.
25. The Economist. “Western Firms Are Quaking as China’s Electric-Car Industry
Speeds Up.” The Economist, 11 Jan. 2024,
www.economist.com/briefing/2024/01/11/western-firms-are-quaking-aschinas-electric-car-industry-speeds-up. Accessed 2 Aug. 2024.
26. Timo Möller. “The Battery Chemistries Powering the Future of Electric
Vehicles.” McKinsey & Company, 14 Nov. 2024,
www.mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-and-assembly/our-insights/thebattery-chemistries-powering-the-future-of-electric-vehicles. Accessed 20 Nov. 2024.
27. Washington, D. UNITED STATES SECURITIES and EXCHANGE COMMISSION ANNUAL REPORT pursuant to SECTION 13 or 15(D) of the SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT of 1934 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS.
www.sec.gov/files/form10-k.pdf.
